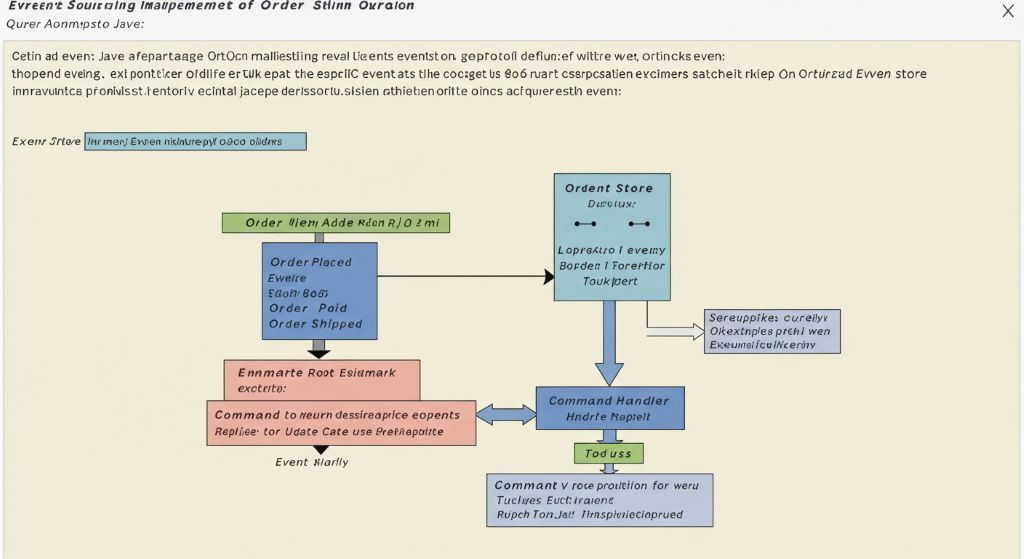
Event Sourcing (이벤트 소싱) 패턴은 애플리케이션의 현재 상태(Current State) 대신, 그 상태를 만들어낸 모든 **변경 이력(Events)**을 순서대로 저장하는 방식입니다. 현재 상태는 이 이벤트들의 스트림을 재생(Replay)하여 재구성합니다.
이 패턴을 Java로 구현한 간단한 은행 계좌 시스템 샘플을 Spring Boot 환경을 가정하여 작성해 드립니다.
🏦 Event Sourcing Java 샘플: 은행 계좌
1. 이벤트 객체 정의 (Events)
모든 상태 변경은 불변(Immutable) 이벤트 객체로 정의됩니다.
Java
// BaseEvent.java
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
public abstract class BaseEvent {
protected String aggregateId;
protected LocalDateTime timestamp = LocalDateTime.now();
protected int version;
// Getters and Setters...
public String getAggregateId() { return aggregateId; }
public void setAggregateId(String aggregateId) { this.aggregateId = aggregateId; }
public LocalDateTime getTimestamp() { return timestamp; }
public int getVersion() { return version; }
public void setVersion(int version) { this.version = version; }
}
// AccountCreatedEvent.java
public class AccountCreatedEvent extends BaseEvent {
private String owner;
private double initialBalance;
public AccountCreatedEvent(String aggregateId, String owner, double initialBalance) {
this.aggregateId = aggregateId;
this.owner = owner;
this.initialBalance = initialBalance;
}
// Getters...
public String getOwner() { return owner; }
public double getInitialBalance() { return initialBalance; }
}
// FundsDepositedEvent.java
public class FundsDepositedEvent extends BaseEvent {
private double amount;
public FundsDepositedEvent(String aggregateId, double amount) {
this.aggregateId = aggregateId;
this.amount = amount;
}
// Getters...
public double getAmount() { return amount; }
}
// FundsWithdrawnEvent.java
public class FundsWithdrawnEvent extends BaseEvent {
private double amount;
public FundsWithdrawnEvent(String aggregateId, double amount) {
this.aggregateId = aggregateId;
this.amount = amount;
}
// Getters...
public double getAmount() { return amount; }
}
2. Aggregate (도메인 모델)
이벤트들을 처리하고 현재 상태를 재구성하는 도메인 객체입니다.
Java
// AccountAggregate.java
import java.util.List;
public class AccountAggregate {
private String id;
private String owner;
private double balance;
private int version = 0;
// 현재 상태를 이벤트 목록으로 재구성
public void replay(List<BaseEvent> history) {
for (BaseEvent event : history) {
apply(event);
this.version = event.getVersion(); // 이벤트 버전을 현재 버전으로 업데이트
}
}
// 각 이벤트를 적용하여 상태 변경
public void apply(BaseEvent event) {
if (event instanceof AccountCreatedEvent) {
handle((AccountCreatedEvent) event);
} else if (event instanceof FundsDepositedEvent) {
handle((FundsDepositedEvent) event);
} else if (event instanceof FundsWithdrawnEvent) {
handle((FundsWithdrawnEvent) event);
}
}
// --- 이벤트 핸들러 ---
private void handle(AccountCreatedEvent event) {
this.id = event.getAggregateId();
this.owner = event.getOwner();
this.balance = event.getInitialBalance();
System.out.printf(" [Apply] 계좌 생성: ID=%s, 잔액=%.2f\n", id, balance);
}
private void handle(FundsDepositedEvent event) {
this.balance += event.getAmount();
System.out.printf(" [Apply] 입금됨: +%.2f, 현재 잔액=%.2f\n", event.getAmount(), balance);
}
private void handle(FundsWithdrawnEvent event) {
// 출금 시 잔액 검사 로직은 보통 Command Service에서 처리하지만, 여기서는 상태 변경만 반영
this.balance -= event.getAmount();
System.out.printf(" [Apply] 출금됨: -%.2f, 현재 잔액=%.2f\n", event.getAmount(), balance);
}
// Getters
public String getId() { return id; }
public double getBalance() { return balance; }
public int getVersion() { return version; }
}
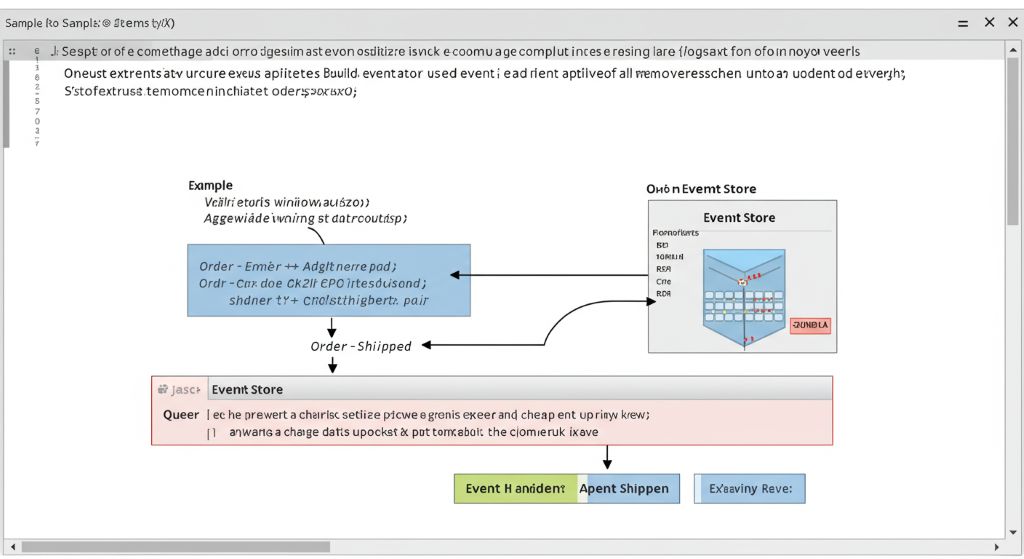
3. 이벤트 저장소 시뮬레이션 (Event Store)
실제로는 Kafka 또는 전용 이벤트 저장소(Event Store DB)를 사용하지만, 여기서는 간단한 List를 사용합니다.
Java
// EventStore.java (실제 DB 역할)
import java.util.*;
public class EventStore {
// Key: Aggregate ID, Value: 해당 Aggregate의 모든 이벤트 목록
private final Map<String, List<BaseEvent>> store = new HashMap<>();
public List<BaseEvent> getEvents(String aggregateId) {
// 해당 Aggregate의 전체 이벤트 이력 반환
return store.getOrDefault(aggregateId, Collections.emptyList());
}
public void saveEvents(String aggregateId, List<BaseEvent> newEvents) {
List<BaseEvent> currentEvents = store.computeIfAbsent(aggregateId, k -> new ArrayList<>());
// 새로운 이벤트에 버전 정보 부여
int nextVersion = currentEvents.size() + 1;
for (BaseEvent event : newEvents) {
event.setVersion(nextVersion++);
currentEvents.add(event);
}
System.out.printf("[EventStore] %s의 새 이벤트 %d개 저장됨.\n", aggregateId, newEvents.size());
}
}
4. Command Service (이벤트 생성 및 저장)
클라이언트의 요청을 받아 이벤트를 생성하고 EventStore에 저장하는 서비스입니다.
Java
// AccountCommandService.java
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.UUID;
public class AccountCommandService {
private final EventStore eventStore;
public AccountCommandService(EventStore eventStore) {
this.eventStore = eventStore;
}
// Command: 계좌 생성 요청
public String createAccount(String owner, double initialBalance) {
String accountId = UUID.randomUUID().toString().substring(0, 8);
AccountCreatedEvent event = new AccountCreatedEvent(accountId, owner, initialBalance);
eventStore.saveEvents(accountId, Arrays.asList(event));
return accountId;
}
// Command: 입금 요청
public void depositFunds(String accountId, double amount) {
// 1. 현재 상태 로드 (이벤트 리플레이)
List<BaseEvent> history = eventStore.getEvents(accountId);
AccountAggregate aggregate = new AccountAggregate();
aggregate.replay(history);
// 2. 비즈니스 로직 검증 (예: 계좌 존재 여부)
if (aggregate.getId() == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("계좌를 찾을 수 없습니다: " + accountId);
}
// 3. 새 이벤트 생성 및 저장
FundsDepositedEvent event = new FundsDepositedEvent(accountId, amount);
eventStore.saveEvents(accountId, Arrays.asList(event));
}
// Command: 출금 요청
public void withdrawFunds(String accountId, double amount) {
// 1. 현재 상태 로드 (이벤트 리플레이)
List<BaseEvent> history = eventStore.getEvents(accountId);
AccountAggregate aggregate = new AccountAggregate();
aggregate.replay(history);
// 2. 비즈니스 로직 검증 (예: 잔액 부족)
if (aggregate.getBalance() < amount) {
throw new IllegalStateException("잔액이 부족합니다. 현재 잔액: " + aggregate.getBalance());
}
// 3. 새 이벤트 생성 및 저장
FundsWithdrawnEvent event = new FundsWithdrawnEvent(accountId, amount);
eventStore.saveEvents(accountId, Arrays.asList(event));
}
}
5. 메인 클래스 (실행)
Java
// MainApplication.java
import java.util.List;
public class MainApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
EventStore eventStore = new EventStore();
AccountCommandService commandService = new AccountCommandService(eventStore);
System.out.println("--- 1. 계좌 생성 Command ---");
String accountId = commandService.createAccount("홍길동", 1000.0);
System.out.println("생성된 계좌 ID: " + accountId);
System.out.println("\n--- 2. 입금 Command ---");
commandService.depositFunds(accountId, 500.0);
System.out.println("\n--- 3. 출금 Command (성공) ---");
commandService.withdrawFunds(accountId, 200.0);
// 최종 상태 조회 (이벤트 리플레이)
System.out.println("\n--- 4. 최종 계좌 상태 조회 (Replay) ---");
List<BaseEvent> history = eventStore.getEvents(accountId);
AccountAggregate finalAccount = new AccountAggregate();
System.out.println(">>> 이벤트 이력 재생 시작 (" + history.size() + "개):");
finalAccount.replay(history);
System.out.printf("\n[Final State] 계좌 ID: %s, 소유주: %s, 최종 잔액: %.2f, 최종 버전: %d\n",
finalAccount.getId(), "홍길동", finalAccount.getBalance(), finalAccount.getVersion());
// 출금 실패 시나리오
System.out.println("\n--- 5. 출금 Command (실패 시나리오) ---");
try {
// 잔액은 현재 1000 + 500 - 200 = 1300.0 입니다. 2000.0 출금 시도.
commandService.withdrawFunds(accountId, 2000.0);
} catch (IllegalStateException e) {
System.err.println("[Command Fail] 오류 발생: " + e.getMessage());
// 실패했기 때문에 새로운 이벤트는 저장되지 않습니다.
}
}
}
실행 결과 (예시)
--- 1. 계좌 생성 Command ---
[EventStore] <ID>의 새 이벤트 1개 저장됨.
생성된 계좌 ID: <ID>
--- 2. 입금 Command ---
>>> 이벤트 이력 재생 시작 (1개):
[Apply] 계좌 생성: ID=<ID>, 잔액=1000.00
[EventStore] <ID>의 새 이벤트 1개 저장됨.
--- 3. 출금 Command (성공) ---
>>> 이벤트 이력 재생 시작 (2개):
[Apply] 계좌 생성: ID=<ID>, 잔액=1000.00
[Apply] 입금됨: +500.00, 현재 잔액=1500.00
[EventStore] <ID>의 새 이벤트 1개 저장됨.
--- 4. 최종 계좌 상태 조회 (Replay) ---
>>> 이벤트 이력 재생 시작 (3개):
[Apply] 계좌 생성: ID=<ID>, 잔액=1000.00
[Apply] 입금됨: +500.00, 현재 잔액=1500.00
[Apply] 출금됨: -200.00, 현재 잔액=1300.00
[Final State] 계좌 ID: <ID>, 소유주: 홍길동, 최종 잔액: 1300.00, 최종 버전: 3
--- 5. 출금 Command (실패 시나리오) ---
>>> 이벤트 이력 재생 시작 (3개):
[Apply] 계좌 생성: ID=<ID>, 잔액=1000.00
[Apply] 입금됨: +500.00, 현재 잔액=1500.00
[Apply] 출금됨: -200.00, 현재 잔액=1300.00
[Command Fail] 오류 발생: 잔액이 부족합니다. 현재 잔액: 1300.0